Electron Domain Geometry Definition
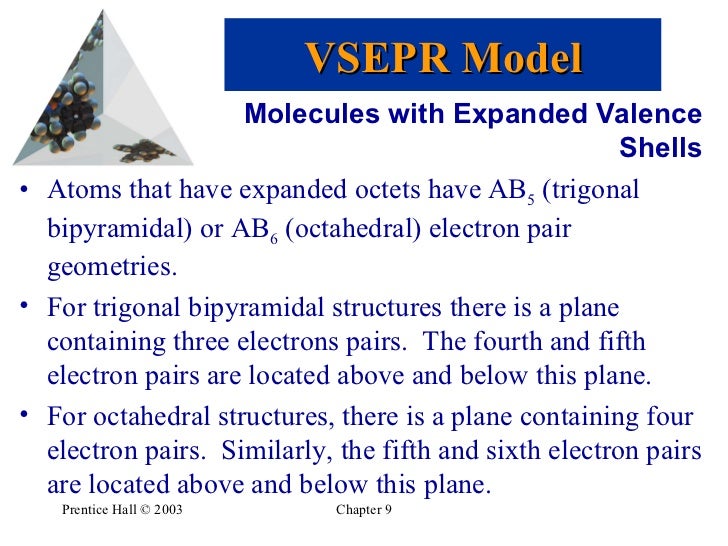
To apply our Electron Domain model to understand this geometry we must place six points representing the six electron pairs about the central ceS atom on the surface of a sphere with maximum distances between the points. The most stable electron-domain geometry for five electron domains is the trigonal bipyramid two trigonal pyramids sharing a base.
An atoms electron domain is the number of lone pairs or chemical bond locations that surround it.

Electron domain geometry definition. Electron geometry which is the geometric arrangement of the ELECTRON groups around an atom that is based on the total number of electron pairs Electron domain geometries is the total number of electron pairs both bonding and lone pairs. A model that accounts for the geometric arrangements of shared and unshared electron pairs around a central atom in terms of the repulsions between electron pairs. The VSEPR theory states that electron pairs located around a certain atom repel each other.
The molecular geometries also called shapes of molecules are determined experimentally by X-ray diffraction. However if there is a lone pair the lone pair doesnt form a bond and therefore doesnt contribute to the shape of the whole molecule. A single double or triple bond or a lone pairElectron domains repel each other and therefo.
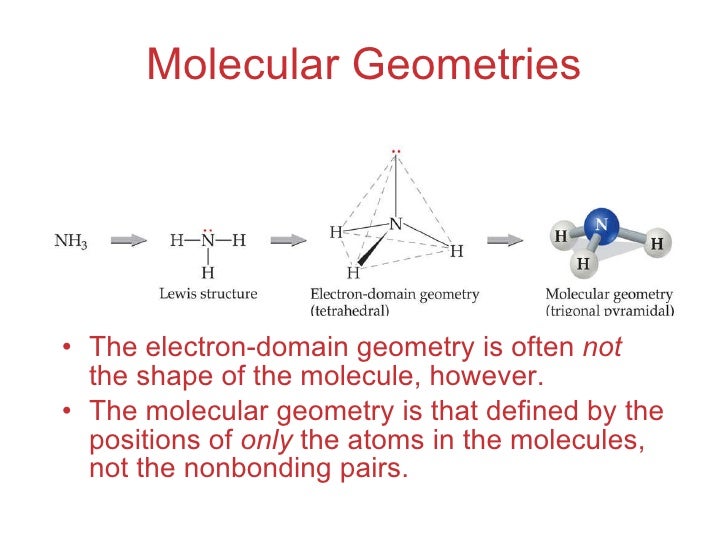
By knowing the electron domain of each atom in a molecule you can predict its geometry. It is the 3D arrangement of all the atoms in a particular molecule. The electron domain geometry is also tetrahedral because we have zero non-bonding pairs on the central atom.
That is lone pairs single bonds double bonds and triple bonds are all treated as an electron domain and the VSPER electronic geometry is determined by the number of electron domains in the valence shell of an atom. If there is no lone pair all the electron domains form bonds and the electron domain geometry is the same as molecular geometry. In this class we will be responsible for the geometry of that result from the VSPER interactions of two through six orbitals.
The term electron-pair geometry is the name of the geometry of the electron-pairgroupsdomains on the central atom whether they are bonding or non-bonding. Also called charge centers also called charge centresSpoiler. Even though the lone pairs.
The requisite geometry is found in fact to be that of an octahedron in agreement with the observed geometry. These electron pairs can be either bonding electrons or non-bonding electrons. It represents the number of locations expected to contain electrons.
Learn definitions molecular geometry electron domain with free interactive flashcards. Molecular geometry is the name of the geometry used to describe the shape of a molecule. Unlike the electron-domain geometries we have seen to this point the electron domains in a trigonal bipyramid can point toward two geometrically distinct types of positions.
The 3D arrangement of the electron domains around an atom according to the VSEPR. Learn definitions molecular geometry electron domain chemistry with free interactive flashcards. Electron geometry teaches us about the arrangement of different electron groups.
Additionally how do you determine the number of electron domains in a molecule or ion. Define ionization energy and identify ionization trends on the periodic table. Molecular Geometries from each Electron Domain Geometry Since electron pairs cannot be seen the electron domain geometries are theoretical.
Choose from 500 different sets of definitions molecular geometry electron domain flashcards on Quizlet. Electron geometry is the shape of a molecule predicted by considering both bond electron pairs and lone electron pairs. A molecule can have a different shape when referring to its electron-domain geometry than when referring to its molecular geometry.
Choose from 500 different sets of definitions molecular geometry electron domain chemistry flashcards on Quizlet. This is because electrons distribute around an atom to minimize repulsion with one another. Trigonal planar trigonal pyramidal.
What is the electron domain geometry EDG and molecular geometry MG of AsH 3. For example sulfur dioxide SO2 electron-domain geometry is trigonal planar. Molecular geometry on the other hand helps us understand the entire atom and its arrangement.
 Vsepr Theory Geometry Of Organic Molecules Chemistry Steps
Vsepr Theory Geometry Of Organic Molecules Chemistry Steps
Difference Between Electron Geometry And Molecular Geometry Difference Between

 What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Sf 5 Study Com
What Is The Molecular Geometry Of Sf 5 Study Com
 What Is Molecular Geometry Of Ab5 And Ab6 Type Compounds
What Is Molecular Geometry Of Ab5 And Ab6 Type Compounds
 Molecular Geometries And Bonding Theories Ppt Video Online Download
Molecular Geometries And Bonding Theories Ppt Video Online Download
 Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Vsepr
Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Vsepr
 Chapter 9 Lecture Molecular Geometry
Chapter 9 Lecture Molecular Geometry
 What Are The Differences In Shapes Between Molecular Geometry And Electronic Geometry Chemistry Stack Exchange
What Are The Differences In Shapes Between Molecular Geometry And Electronic Geometry Chemistry Stack Exchange
Http Www Quimica Ufpr Br Edulsa Cq167 Moleculargeometry Pdf
 Ch 9 Molecular Geometry Diagram Quizlet
Ch 9 Molecular Geometry Diagram Quizlet
 O3 Molecular Geometry Shape And Bond Angles Youtube
O3 Molecular Geometry Shape And Bond Angles Youtube
 Counting Electron Domains And Determining Electron Domain Geometries Youtube
Counting Electron Domains And Determining Electron Domain Geometries Youtube
Difference Between Electron Geometry And Molecular Geometry Definition Identification Examples
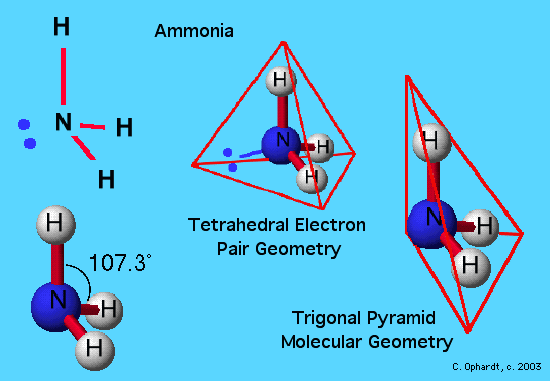 Trigonal Pyramidal Molecular Geometry Chemistry Libretexts
Trigonal Pyramidal Molecular Geometry Chemistry Libretexts
 6 3 Molecular Shape Introductory Chemistry
6 3 Molecular Shape Introductory Chemistry
 What Is The Difference Between Electron Domain Geometry Molecular Geometry Youtube
What Is The Difference Between Electron Domain Geometry Molecular Geometry Youtube